Unit 3 - Diet and nutritional treatment approach for dysphagia
3.2. Balanced diet
3.2.2. Distribution of foodstuffs on a balanced diet
A balanced diet gives the body the nutrients it needs to function correctly. In order to get the nutrients needed, most of the daily caloric intake in should come from:
-
fresh fruits & vegetables;
-
whole grains;
-
protein rich foods (legumes; meat; fish)
-
dairy products;
-
fats and oils
In practice, a balanced diet means that we should eat a variety of foods, in different proportions, and in general avoid leaving out entire food groups, as each food group provides fuel and nutrients required for optimal health.
Food-Based Dietary Guidelines (FBDG) are developed to help people build a balanced and varied diet by following the food groups and consuming them in the right proportions.
-
Food-Based Dietary Guidelines (FBDG) in Europe
FBDG advice on foods, food groups and dietary patterns to provide the required nutrients to the general public to promote overall health and prevent chronic diseases
Some
countries provide a graphic representation, such as a food pyramid or
a plate, to illustrate and sum-up the advice.

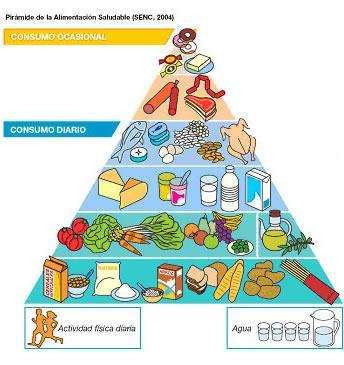
Watch
this video to learn what are and how to use Dietary Guidelines:

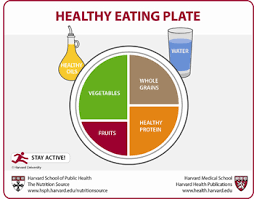
The Harvard Eating Plate is more widely accepted nowadays than the Food Pyramid. Find out more
here: https://www.hsph.harvard.edu/nutritionsource/healthy-eating-plate/
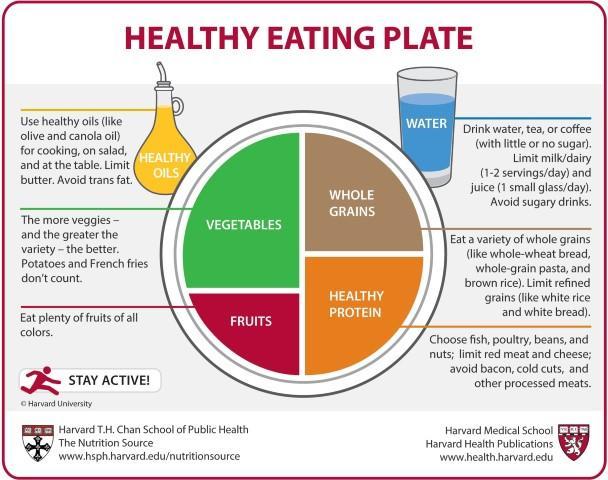
-
A balanced diet consists on:
-
Fruits & Vegetables should make up the largest portion of our diet. They contain a wide variety of nutrients like several vitamins and minerals, carbohydrates and dietary fibre. They are also the main source of phytochemicals.

Source: designed by Canva Pro
-
It is recommended to choose mostly whole grains (such as brown rice, oats and barley), and whole meal/wholegrain/high cereal/fibre varieties of bread, pasta, crispbreads and cereal foods. They mainly provide starch and fiber, but they are sources of several important vitamins and minerals.

Source: designed by Canva Pro
-
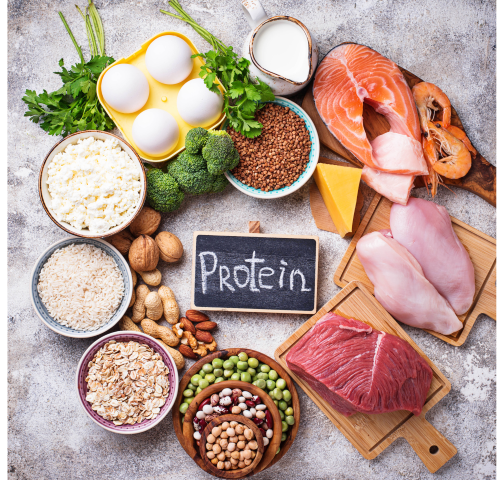
Varied protein rich foods
 Dairy
products as milk, natural yoghurt or cheese, primarily provide us
with calcium, protein and fats, plus other vitamins and minerals.
Dairy
products as milk, natural yoghurt or cheese, primarily provide us
with calcium, protein and fats, plus other vitamins and minerals.
Red meat is high in saturated fat, vitamin B12, iron, niacin, and zinc. Meanwhile, fish is a great source of omega-3 fatty acids, vitamin D, thiamine, selenium, and iodine.
Vitamin A, B12, iron, and selenium are present in significant amounts in liver and other organ meats. These meats are also excellent sources of choline, an important nutrient for brain, muscle, and liver health.
Meat is a rich source of protein and several vitamins and minerals, including vitamin B12, niacin, and selenium.
Source: obtained from Canva Pro
-
Use healthy fats.
Olive oil, canola oil and seed oils are useful for cooking and are sources of heart-healthymonounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats. Tree nuts and fish are also sources of healthypolyunsaturated fats, including omega-3s.

Source: obtained from Canva Pro
-
Choose water as your main drink, and avoid sugary options such as soft drinks, sports drinks and energy drinks.
Drink fluids, even you don’t feel thirst!
Source: obtained from Canva Pro
-
Seasoning. Herbs and spices provide a wonderful range of flavours and aromas to our food. Limit added salt and sugar.


Source: obtained from Canva Pro Source: designed by Canva Pro
-
Mediterranean Diet: healthy and sustainable dietary pattern
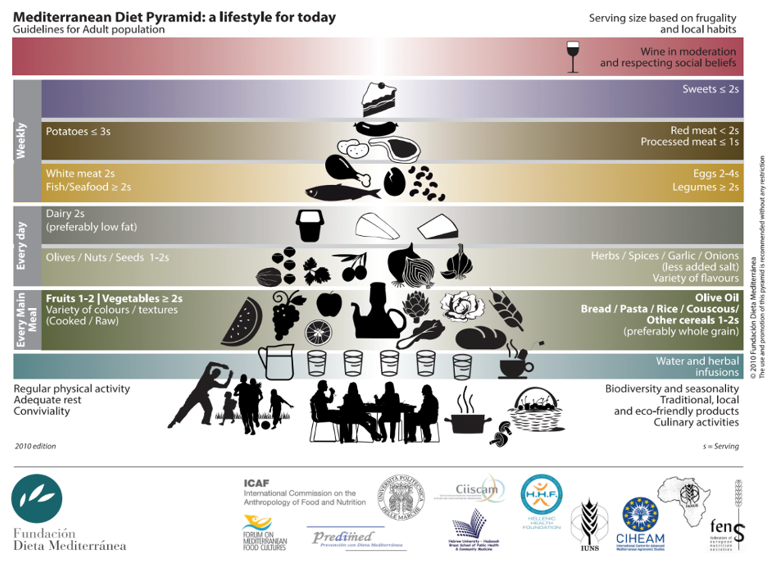
Find out more about Mediterranean Diet here: https://dietamediterranea.com/
