Unit 2 - Care and nutrition (e-book)
Lesson 2.1. Nursing and feeding techniques and equipment
2.1.4. Alternative feeding methods: artificial nutrition
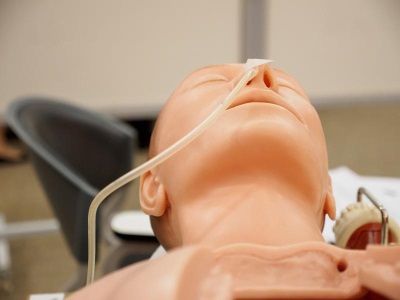
Enteral feeding
Enteral feeding is a method of supplying nutrients directly into the gastrointestinal tract with tube or ostomy. A person on enteral feeds usually has a condition or injury that prevents eating a regular diet by mouth, but their GI tract is still able to function. Being fed through a tube allows them to receive nutrition and keep their GI tract working. Enteral feeding may make up their entire caloric intake or may be used as a supplement.
Source: https://pixabay.com
Nasogastric (NG tube) tube is a small and special tube that goes into the stomach through the nose. Liquid food and medicines are given through the tube directly into the stomach, giving a person extra calories.
Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy (PEG) is a procedure in which a flexible feeding tube is placed through the abdominal wall and into the stomach. PEG allows nutrition, fluids and/or medications to be put directly into the stomach, bypassing the mouth and esophagus.
Parenteral nutritionParenteral nutrition (PN) or intravenous feeding, is a method of getting nutrition into your body through your veins. It include protein, carbohydrate, fat, minerals and electrolytes, vitamins and other trace elements for patients who cannot eat or absorb enough food through tube feeding formula or by mouth to maintain good nutrition status. Achieving the right nutritional intake in a timely manner can help combat complications and be an important part of a patient’s recovery. Parenteral nutrition is sometimes called Total Parenteral Nutrition (TPN). It is used in people whose digestive function is compromised or needs rest for therapeutic reasons for more than 5 - 7 days.
Videos:
Enteral feeding:
Parenteral
nutrition: