Unit 3 - Nutrition (e-book)
3.3 Nutrition for special requirements
3.3.1 Allergies and intolerances
Food allergies
 A food allergy happens when the body's immune system, which normally fights
infections, sees the food as an invader. This leads to an allergic reaction —
immune systems response in which chemicals likes histamine are released in the
body. The reaction can cause symptoms like hives, vomiting, belly pain, throat
tightness, hoarseness, coughing, breathing problems, or a drop in blood
pressure. Sometimes it can lead to death.
A food allergy happens when the body's immune system, which normally fights
infections, sees the food as an invader. This leads to an allergic reaction —
immune systems response in which chemicals likes histamine are released in the
body. The reaction can cause symptoms like hives, vomiting, belly pain, throat
tightness, hoarseness, coughing, breathing problems, or a drop in blood
pressure. Sometimes it can lead to death.
European union food law has identified 14 allergens as ingredients in the food and drink as the most potent and prevalent allergens.
Figure 20. Food Allergens
(Source: CPD Online College Knowledge base)
Food intolerance
A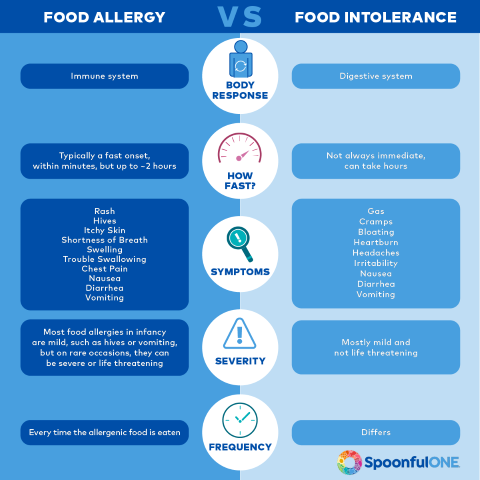 food intolerance means either the body can't properly digest the food
that is eaten, or that a particular food might irritate the digestive
system. It doesn't involve your immune system and it is never
life-threatening.
food intolerance means either the body can't properly digest the food
that is eaten, or that a particular food might irritate the digestive
system. It doesn't involve your immune system and it is never
life-threatening.
Symptoms of food intolerance happen gradually, often a few hours after eating the problem food, and it can include nausea, gas, cramps, belly pain, diarrhea, irritability, or headaches.
Figure 21. Food Allergy and Intolerances (Source: Spoonfulone)