Unit 3 - Nutrition (e-book)
| Website: | IDEC TrainingCentre elearning |
| Kurs: | MODULE 2: CAREGIVERS, FAMILIES AND PEOPLE WITH DYSPHAGIA |
| Buch: | Unit 3 - Nutrition (e-book) |
| Gedruckt von: | Nepřihlášený host |
| Datum: | Mittwoch, 4. Februar 2026, 18:03 |
3.1 Basics of nutrition on dysphagia condition
3.1.1 Explanation about the importance of dysphagia nutrition
Effective nutritional management is crucial to the health of patients with dysphagia.
Early intervention by a clinical nutritionist is very important to indicate the dietary guidelines to follow.
Appropriate and timely nutritional intervention can play a vital role in the prevention of dysphagia health complications, dehydration, malnutrition and promotion of recovery.
Goals of nutrition management are:
- To maintain and ensure adequate nutrition and hydration status – because dysphagia can result in reduced or altered oral intake of food/liquid.
- Apply the modified diet with a correct and safe texture following the recommendations of the speech therapist. Foods with inappropriate textures can cause choking and other health complications.
- Ensure adequate and ample intake of nutritious and safe foods.

Figure 1. Nutrients (Source: designed by Canva Pro)
3.1.2 Food and nutrients (macronutrients and micronutrients)
Cambridge Dictionary defines nutrient as any substance that plants or animals need in order to live and grow. Nutrients are ingested through the diet and can be classified into: macronutrients and micronutrients.
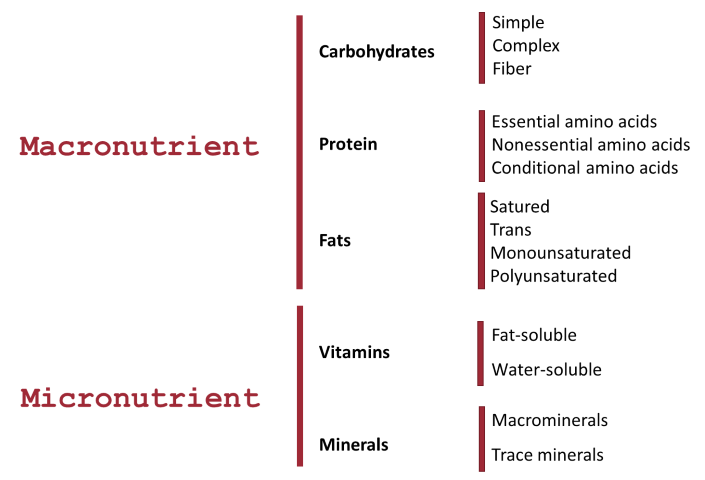
Figure 2. Diet Nutrients
(Source: designed by CADIS HUESCA)
Macronutrient
Nutrients that predominate in the composition of food and, therefore, those ingested in greater quantities (grams). Their main functions within the organism are energetic and structural.
Carbohydrates and fibers
Carbohydrates provide most of the body’s energy. They are present in healthful, processed and low nutritional values foods. They are classified into three types:
Simple carbohydrates.
Or sugars are made up of shorter chains of molecules and are faster to digest the body with a quick and short-lived source of energy.
Examples of foods containing them: fruits, jams, honey, white bread, sweets, date, syrup, milk, sugar, others.
Complex carbohydrates.
They are made up of long chains of molecules that are absorbed by the body more slowly and for a longer period of time.
Examples of foods containing them: vegetables, whole grains, fruits, natural nuts, legumes and others.
Fiber.
It is a complex carbohydrates.
Examples of foods containing them: vegetables, whole grains, fruits with skin, natural nuts, legumes and others.

Figure 3. Carbohydrates and fiber (Source: designed by Canva Pro)
Protein
Proteins are molecules made up of amino acids and they are essential of life. The protein sources could be vegetables and/or animal based. When proteins are digested, they broken down into amino acids. Examples of foods containing them: meats (beef, sheep, pork, rabbit, chicken...), white and blue fish (sardines, tuna, sea bream, sole...), seafood, eggs, legumes and others.

Figure 4. Protein (Source: obtained from Canva Pro)

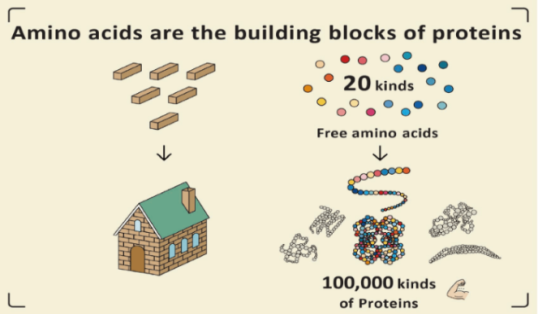
Figures 5 & 6. Amino acids are part of food. Amino acids form the proteins that compose us. (Source: https://www.ajinomoto.com/es/aboutus/amino-acids/what-are-amino-acids)
-
Essential amino acids.
It cannot be made by the body. As a result, they must come from food.
-
Nonessential amino acids
Nonessential means that our bodies can produce the amino acid, even if we do not get it from the food we eat.
-
Conditional amino acids.
Conditional amino acids are usually not essential, except in times of illness and stress.
Fats
Fat is the nutrient that provides the most energy compared to the others and helps the body absorb some vitamins. The fat sources could be vegetables and/or animal based.
-
Satured.
Most animal fats are saturated and experts recommend a diet low in saturated fat. They are popular with manufacturers of processed foods. they are typically solid at room temperature and can cause problems with your cholesterol levels, which can increase your risk of heart disease. For example: butter, ghee, suet, lard, coconut oil and palm oil.
- Monounsaturated.
-
Trans.
They are unhealthy. Examples: fried doughnuts, and baked goods including cakes, pie crusts, biscuits, frozen pizza, cookies, crackers, and stick margarines.
Polyunsaturated.
They are good for health. For example: olive oil, soybean oil, corn oil, sunflower oil, etc.

Figure 7. Fats (Source: obtained from Canva Pro)
M icronutrient
icronutrient
Micronutrients, often referred to as vitamins and minerals, are essential for healthy development, disease prevention, and wellbeing. People only need small amounts of micronutrients.
Figure 8. Micronutrient. (Source: Health vector created by freepik – www.freepik.com)
Vitamins
Vitamins are organic compounds that people need in small quantities. Vitamins need to come from food because the body either does not produce them or produces very little. A balanced diet usually provides enough of these vitamins. They can be classified into:
-
Water-soluble vitamins.
-
Fat-soluble vitamins
Minerals
Minerals are divided into major minerals (macrominerals), which are needed in larger amounts, and trace minerals (microminerals), which are needed in smaller amounts.
A balanced diet usually provides all of the essential minerals.

Figure 9. Food and nutrition Infographic (Source: designed by Canva Pro)
Infographics available for download on the training platform (https://indeed-project.org/)
3.2 Balanced diet
A balanced diet is one that fulfills all of a person’s nutritional needs because provides all the nutrients a person requires. Humans need a certain amount of calories and nutrients to stay healthy.
3.2.1 Distribution of foodstuffs on a balanced diet
Vegetables and fruits

Figure 10. Vegetables and fruits (Source: designed by Canva Pro)
Plant foods should make up the largest portion of our diet. Plant foods contain a wide variety of nutrients like vitamins, minerals, phytochemicals and antioxidants. They are also the main source of carbohydrates and fibre in our diet. A diet rich in vegetables decreases health problems.
Grains

Figure 11. Grains (Source: designed by Canva Pro)
Grains food group it is recommend to choose mostly whole grains (such as brown rice, oats and barley), and wholemeal/wholegrain/high cereal/fibre varieties of bread, pasta, crisp breads and cereal foods (over highly processed, refined varieties).
The quality of the carbohydrates you eat is at least as important as the quantity to better health.
Protein
Protein is an essential nutrient. In addition to providing protein, it also contains other nutrients such as fats, vitamins and minerals. It is important to combine animal and vegetable proteins.
The consumption of quality protein is more important to our health than the quantity consumed.

Figure 12. Protein (Source: designed by Canva Pro)
Healthy fats

Figure 13. Healthy fats (Source: designed by Canva Pro)
Fat is an important part of a healthy diet. Choosing healthy, quality fats in the diet is preferable to eating a low-fat diet. It is preferable to consume "good" unsaturated fats - monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, limit foods high in saturated fats and avoid "bad" fats - trans fats.
Choose Water
Water is the best drink to stay hydrated and it supports many other
essential functions in the body. Choose water as your main drink, and
avoid sugary options such as soft drinks, sports drinks and energy
drinks.
We drink fluids when we feel thirst, the major signal alerting us when our body runs low on water but sometimes we drink not based on these factor.
Figure 14. Choose water (Source: designed by Canva Pro)
Enjoy herbs and spices
Herbs and spices provide a wonderful range of flavours and aromas to
our food. They have health-promoting properties, but since we tend to
eat them in smaller amounts their primary purpose is to flavour and
colour our meals.
It is an easy way to create foods that suit your tastes and increase your enjoyment of home-made meals without needing to use salt when cooking or eating.
Figure 15. Herbs and spices (Source: designed by Canva Pro)

Limit added salt and sugar
It is important to limit our intake of added salt and sugar.
Figure 16. Salt and sugar (Source: designed by Canva Pro)
Healthy eating guidelines
Healthy Eating Plate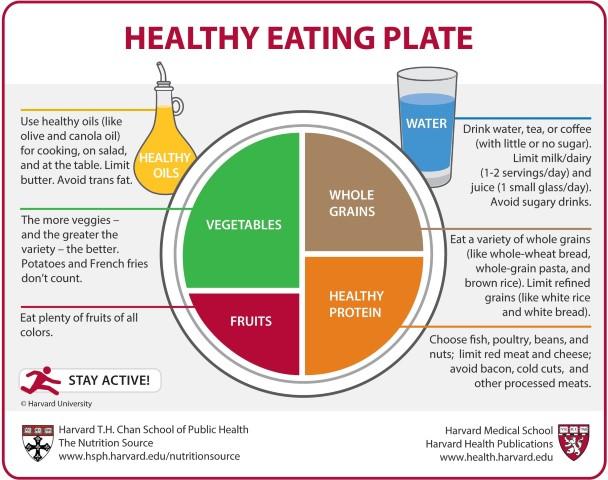
The Healthy Eating Plate is another simple guide for a healthier, well-balanced meal that includes all the food groups in the right proportions. It’s the easy way to get all the nutrients that your body needs regardless of the meal type, cuisine or occasion. It was owned by Harvard University.
Figure 17. Healthy Eating Plate. Copyright © 2011, Harvard University. For more information about The Healthy Eating Plate, please see The Nutrition Source, Department of Nutrition, Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, www.thenutritionsource.org, and Harvard Health Publications, www.health.harvard.edu.

Healthy Eating Pyramid
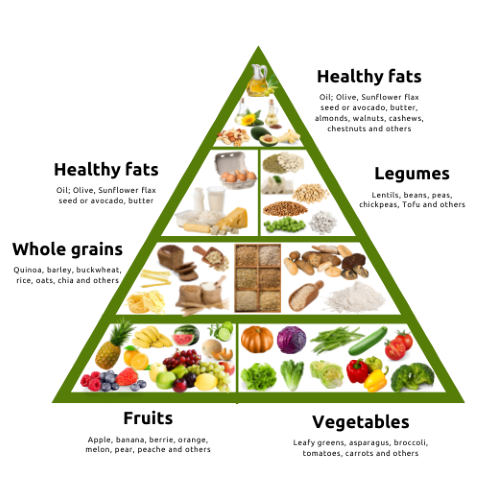
The Healthy Eating Pyramid is a simple visual guide to explain a balanced diet based on the recommended food intake for 19–50 year-olds, according to the Australian Dietary Guidelines (2013). It shows the types and proportion of foods that we should eat every day for good health.
Figure 18. Healthy Eating Pyramid.
The Australian Nutrition Foundation Inc. 3rd edition, 2015
Practical exercises to apply the theory
In this exercise we will become aware of the importance of a balanced diet.
Materials: not necessary
Exercise: Reflect on the importance of a balanced diet. Recall the foods you have eaten in the last 7 days and answer the following questions:
Do you consume foods from all food groups each day?
Do your meals resemble the composition of the Harvard plate?
What aspects of your diet do you think are healthy?
What aspects of your diet do you think could be improved?

Figure 19. Distribution of foodstuffs on a balanced diet Infographic (Source: designed by Canva Pro)
Infographics available for download on the training platform (https://indeed-project.org/)
3.3 Nutrition for special requirements
3.3.1 Allergies and intolerances
Food allergies
 A food allergy happens when the body's immune system, which normally fights
infections, sees the food as an invader. This leads to an allergic reaction —
immune systems response in which chemicals likes histamine are released in the
body. The reaction can cause symptoms like hives, vomiting, belly pain, throat
tightness, hoarseness, coughing, breathing problems, or a drop in blood
pressure. Sometimes it can lead to death.
A food allergy happens when the body's immune system, which normally fights
infections, sees the food as an invader. This leads to an allergic reaction —
immune systems response in which chemicals likes histamine are released in the
body. The reaction can cause symptoms like hives, vomiting, belly pain, throat
tightness, hoarseness, coughing, breathing problems, or a drop in blood
pressure. Sometimes it can lead to death.
European union food law has identified 14 allergens as ingredients in the food and drink as the most potent and prevalent allergens.
Figure 20. Food Allergens
(Source: CPD Online College Knowledge base)
Food intolerance
A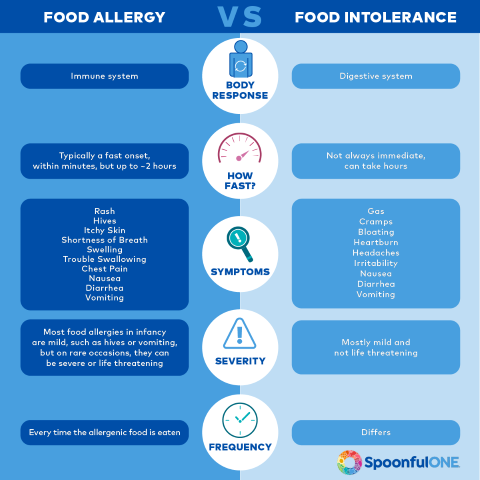 food intolerance means either the body can't properly digest the food
that is eaten, or that a particular food might irritate the digestive
system. It doesn't involve your immune system and it is never
life-threatening.
food intolerance means either the body can't properly digest the food
that is eaten, or that a particular food might irritate the digestive
system. It doesn't involve your immune system and it is never
life-threatening.
Symptoms of food intolerance happen gradually, often a few hours after eating the problem food, and it can include nausea, gas, cramps, belly pain, diarrhea, irritability, or headaches.
Figure 21. Food Allergy and Intolerances (Source: Spoonfulone)
3.3.2 Vegetarian
The vegetarian diet involves abstaining from eating meat, fish and poultry. People often adopt a vegetarian diet for religious, personal reasons or environmental reasons.
Vegetarians may also have dysphagia. These people, as well as those who eat a diet with all food groups, should modify their diet in texture according to guidelines set by a medical professional.
A vegetarian diet should include a diverse mix of fruits, vegetables, grains, healthy fats and proteins.
To replace the protein provided by meat in diet, include a variety of protein-rich plant foods like nuts, seeds, legumes, tempeh, tofu and seitan as well as eggs and dairy products can also boost protein intake.

Figure 22. Vegetarian (Source: obtained from Canva Pro)
 Vegetarians have to avoid the following foods in their diet:
Vegetarians have to avoid the following foods in their diet:
-
Meat: Beef, veal and pork
-
Poultry: Chicken and turkey
-
Fish and shellfish: This restriction does not apply to pescetarians.
-
Meat-based ingredients: Gelatin, lard, carmine, isinglass, oleic acid and suet
-
Other animal products: Vegans may choose to avoid honey, beeswax and pollen.
Figure 23. Vegetarian Pyramid (Source: designed by Canva Pro)
3.4 Samples of texture-modified menu
3.4.1 Balanced menu templates
Balanced menu templatesProper planning of the daily diet ensures a balanced supply of all the nutrients necessary to maintain adequate health through diet.
Eating several meals a day facilitates the consumption of the daily nutritional requirements and allows establishing a routine.
Figure 24. Dietary food intake (Source: designed by Canva Pro)
Next menus are examples of balanced diet based on before healthy eating guidelines. The texture of the food and beverages on these menus should be adapted to the needs of the person with dysphagia destined. Allergies and intolerances should also be taken into account in the menus.
Menu 1 |
|||||||
|
Monday |
Tuesday |
Wednesday |
Thursday |
Friday |
Saturday |
Sunday |
Breakfast |
Coffee with milk Apple cinnamon oatmeal porridge Orange |
Tea with milk Muhlama with whole wheat toast Apple |
Oat milk Rye bread with tomato and cheese Pear |
Coffee with soymilk Banana oatmeal pancakes with dark chocolate |
Oatmeal pourridge with cinnamon and berries |
Coffee with milk Whole wheat toast with avocado Apple |
Fruit and milk smoothie Whole wheat toast with Hummus and tomato |
Mid-Moorning snack |
Handful of nuts |
Tahini cream toast with bananas |
Yogurt |
Strawberries |
Smoothie |
Yogurt |
Handful of pistachio |
Lunch |
Lentil meatballs with lettuce Sausages with tomatoe Plum |
Broccoli with ratatouille Squid with aioli and whole wheat bread Yogurt |
Pureed pumpkin soup Eggplant stuffed with fish Banana |
Green beans with potatoes Hünkar beğendi Pumpkin desert |
Pastitsio Cod with bell pepper sauce Peach |
Silkė pataluose Turkey with apple sauce Yogurt |
Lettuce salad with corn and carrots Balandeliai Bougatsa |
Afternoon Snack |
Yogurt with fruit salad |
Greek yogurt |
Smoothie |
Almond butter, Greek yogurt and sberry jam toast |
Guacamole cream toast |
Smoothie with nut flour |
Berries oatmeal porridge |
Dinner |
Cauliflower with garlic Cod with ratatouille Brownie with orange |
Lettuce and tomato salad Meatballs with almond sauce Pear |
House hors d'oeuvres Potato omelette with aioli and whole wheat bread Yogurt |
Baked vegetables Chicken with vegetables and tomato Roast apple with cinnamon |
Goat cheese salad on toast Keshkek Strawberries |
White asparagus Tenderloin with pepper sauce Duonos |
Sausage with rye bread Salmon with vegetables Yogurt |
Menu 2 |
|||||||
|
Monday |
Tuesday |
Wednesday |
Thursday |
Friday |
Saturday |
Sunday |
Breakfast |
Oat milk Rye bread with avocado and olive oil Banana |
Coffe with milk Banana bread with berries |
Coffee with milk Toast of whole wheat bread with olive oil and tomato |
Coffee with milk Mocha oatmeal Porridge Apple |
Coffee latte with soymilk Banana oatmeal pancakes with honey |
Fruit and milk smoothie Menemen with whole wheat toast |
Unsweetened cocoa milk and oat flakes Portokalopita Mandarin |
Mid-Moorning snack |
Yogurt |
Smoothie with nut flour |
Guacamole cream toast |
Yogurt with fruit pieces |
Handful of almond |
Yogurt |
Smoothie |
Lunch |
Cuban Rice Tenderloin with pepper sauce Apple |
Chesmi nigar soup Chicken with vegetables Cheesecake |
Cheshmi nigar soup Squid with aioli and whole wheat bread Strawberries |
Green beans and potatoes Sausage with rye bread Bougatsa |
Chickpeas with cod Egg with béchamel sauce Pear |
Beet soup Pastitsio Yogurt |
Goat cheese salad on toast Tunna small turnover Muhallebi |
Afternoon Snack |
Peanut butter and banana toast |
Yogurt with fruit pieces |
Orange |
Handful of almond |
Olive oil and tomato toast |
Coffee Latte Silk curd cake |
Hummus cream toast |
Dinner |
Tomato salad with hard-boiled egg and tuna fish Sausages with potato Mandarin |
Pumpkin Puree Spanakopita Rizogalo |
Mixed salad Falafel Greek Yogurt |
Herring in bedding Tunna omelet Οrange |
Pumpkin puree Tomatokeftedes Rizogalo |
Creamed spinach Moussaka Roast pear |
Spaghetti Bolognese Hake in sauce Fruit salad |
3.4.2 More information about menu dishes
BREAKFAST AND SNACKS
Recipe:
Muhlama
Suggested by: Turkey
Youtube
elaboration video:
Sources: View resource

Figure 25. Muhlama. Web nefis.
Recipe: Menemen
Suggested by: Turkey
Youtube
elaboration video:
Sources: View resource

Figure 26. Menemen. Yeme & İçme YouTube.
Recipe: Banana bread
Suggested by: Spain
Youtube
elaboration video:
Sources: View resource

Figure 27. Banana bread. De Rechupete web.
Recipe: Banana oatmeal pancakes
Suggested by: Spain
Youtube
elaboration video:
Sources: View resource

Figure 28 Banana oatmeal pancake. Simply Delicious Web.
Recipe: Avocado Toast
Suggested by: Spain
Youtube elaboration video: https://cookieandkate.com/avocado-toast-recipe/comment-page-2/
Sources: View resource

Figure 29. Avocado Toast. Cookie and kate Web.
Recipe: Oatmeal Porridge
Suggested by: Spain
Youtube
elaboration video:
Sources: View resource

Figure 30. Oatmeal Porridge. The cooking Foodie.
Recipe: Healthy toast ideas
Suggested by: Spain
Youtube elaboration video:
Sources: View resource

Figure 31. Healthy toast ideas. Crispyfoodidea Web.
Recipe: Purus varškės apkepas/ Silk curd cake
Suggested by: Lithuanian
Youtube
elaboration video:
Sources: View resource

Figure 32. Silk curd cake. La Maistas Web.
LUNCH AND DINNERS
Recipe: Pastitsio / Greek baked pasta
Suggested by: Greece
Youtube elaboration video:
Sources: View resource

Figure 33. Pastitsio. Web Dimitra`s dishes.
Recipe: Moussaka
Suggested by: Greece
Youtube elaboration video: https://www.mygreekdish.com/recipe/mousakas/
Sources: View resource

Figure 34. Moussaka. My Greek Dish Web.
Recipe: Spanakopita
Suggested by: Greece
Youtube elaboration video:
Sources: View resource

Figure 35. Spanakopita. My Greek Dish Web.
Recipe: Tomatokeftedes / Santorini Style Tomato Fritters
Suggested by: Greece
Youtube
elaboration video:
Sources: View resource

Figure 36. Tomatokeftedes. Web Dimitra`s dishes.
Recipe: Lentil meatballs
Suggested by: Turkey
Youtube
elaboration video:
Sources: View resource

Figure 37. Lentil meatballs. Nefis Yemek TarifleriYouTube.
Recipe: Cheshmi nigar soup
Suggested by: Turkey
Youtube
elaboration video:
Sources: View resource

Figure 38. Cheshmi nigar soup. Nefis Yemek Tarifleri YouTube.
Recipe: Hünkar beğendi
Suggested by: Turkey
Youtube
elaboration video:
Sources: View resource

Figure 39. Hünkar beğendi. Feriğin elinden YouTube.
Recipe: Keshkek
Suggested by: Turkey
Youtube
elaboration video:
Sources: View resource

Figure 40. Keshkek. Meltem'in Mutfağı YouTube.
Recipe: Ratatouille
Suggested by: Spain
Youtube
elaboration video:
Sources: View resource

Figure 41. Ratatouille. DeRechupete web.
Recipe: Creamed spinach
Suggested by: Spain
Youtube
elaboration video:
Sources: View resource

Figure 42. Creamed spinach. The Stay at home chef web.
Recipe: Spaghetti Bolognese
Suggested by: Spain
Youtube
elaboration video:
Sources: View resource

Figure 43. Spaghetti Bolognese. Recipetineats Web.
Recipe: Green Beans and Potatoes
Suggested by: Spain
Youtube
elaboration video:

Figure 44. Green Beans and Potatoes. Taste of southern Web.
Recipe: Pumpkin Puree
Suggested by: Spain

Figure 45. Pumpkin Puree. Taste of southern Web.
Recipe: Cuban Rice
Suggested by: Spain
Sources: View resource

Figure 46. Spanish Rice Recipe - Cuban Rice. La Cocina de Loli Dominguez.
Recipe: Eggplant stuffed with fish
Suggested by: Spain
Youtube
elaboration video:
Sources: View resource

Figure 47. Eggplant stuffed with fish. Berenjenas Rellenas Web.
Recipe: Tenderloin with pepper sauce
Suggested by: Spain
Youtube
elaboration video:
Sources: View resource

Figure 48. Tenderloin with pepper sauce. DeRechupete Web.
Recipe:
Goat cheese toast on salad
Suggested by: Spain
Youtube
elaboration video:
Sources: View resource

Figure 49. Goat cheese toast on salad. Garlic delight web.
Recipe: Salmon with vegetables
Suggested by: Spain
Youtube elaboration video:
Sources: View resource

Figure 50. Salmon with vegetables. Daniella's Home Cooking web.
Recipe: Spanish omelete
Suggested by: Spain
Youtube
elaboration video:
Sources: View resource

Figure 51. Spanish omelet. Tasty web.
Recipe: Falafel
Suggested by: Turkey
Youtube
elaboration video:
Sources: View Resource

Figure 52. Falafel. The Best Turkish Recipes Web.
Recipe: Silkė pataluose/ Herring in bedding
Suggested by: Lithuanian
Youtube
elaboration video:
Sources: View Resource

Figure 53. Silkė pataluose. Skonių parkas Youtube.
Recipe: Trinta moliūgų sriuba/ Pureed pumpkin soup
Suggested by: Lithuanian
Youtube
elaboration video:
Sources: View Resource

Figure 54. Pureed pumpkin soup. Be Dietų Youtube.
Recipe: Stuffed cabbage rolls (Balandeliai)
Suggested by: Lithuanian
Youtube
elaboration video:
Sources: View Resource

Figure 55. Balandeliai. The spruce Eats Web.
DESSERTS
Recipe:
Duonos, Serbentų ir grietinėlės desertas
Suggested by: Lithuanian
Youtube
elaboration video:
Sources: View Resource

Figure 56. Duonos. Kumutes virtuve Web.
Recipe: Muhallebi
Suggested by: Turkey
Youtube
elaboration video:
Sources: View Resource

Figure 57. Muhallebi. Web nefis.
Recipe: Bougatsa / Phyllo Custard Pie
Suggested by: Greece
Youtube
elaboration video:
Sources: View Resource

Figure 58. Bougatsa. Web akispetretzikis.com
Recipe: Rizogalo
Suggested by: Greece
Youtube
elaboration video:
Sources: View Resoure

Figure 59. Rizogalo. Web Dimitra`s dishes.
Recipe: Portokalopita / Orange cake
Suggested by: Greece
Youtube
elaboration video:
Sources: View Resource

Figure 60. Portokalopita. Web Nikki Glekas.
3.5 Nutritional supplements
Nutritional supplements are products manufactured by the pharmaceutical industry. They are developed with the purpose of being administered to people with deficient nutritional needs.
Supplements for dysphagia's people are prescribed by a health professional only in those cases where there are chronic nutrient deficiencies, either due to insufficient intake through diet, interaction with drugs or other causes.

Figure 61. Examples of Oral nutritional supplementation (Source: designed by CADIS Huesca)
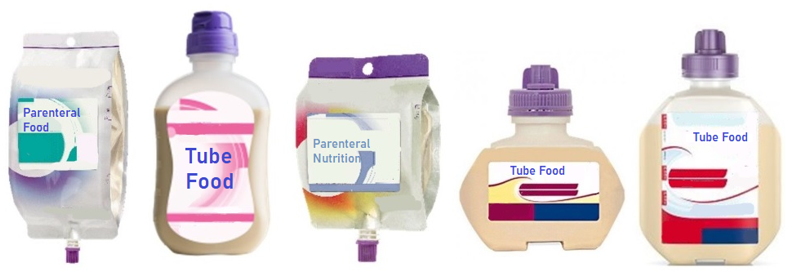
Figure 62. Examples of enteral nutritional supplementation (Source: designed by CADIS Huesca)
3.5.1 Pharmacological treatment in dysphagia
Pharmacological treatment, as with the ingestion of food and beverages, requires proper handling in the mouth and coordination during swallowing.

On many occasions, it is not possible to prepare magistral formulas with other forms due to the instability of the preparation, difficulty in finding the active ingredient, etc, so in these situations the package insert should be read or the pharmacist should be asked for the best way to adapt it.
Figures 63 and 64. Pill drawing (Source: designed by Canva Pro)
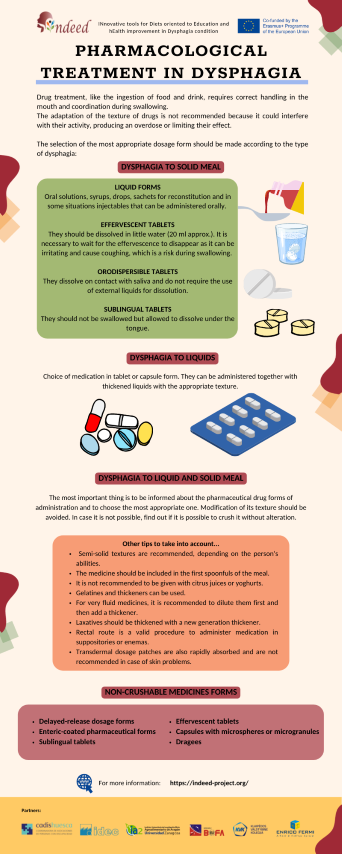
Figure 65. Infographic about pharmacological treatment in dysphagia (Source: designed by Canva Pro)
Infographics available for download on the training platform (https://indeed-project.org/)
Resources
https://nutritionaustralia.org/fact-sheets/healthy-eating-pyramid/
https://www.hsph.harvard.edu/nutritionsource/healthy-eating-plate/
https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/324093#what-is-a-balanced-diet
https://www.healthlinkbc.ca/health-topics/ta3868
https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/002399.htm
https://healthyeating.sfgate.com/two-types-minerals-food-9640.html
https://www.uofmhealth.org/health-library/ta3912
https://www.bonviveur.es/preguntas/que-es-la-piramide-nutricional-australiana
https://nutritionaustralia.org/fact-sheets/healthy-eating-pyramid/
https://www.hsph.harvard.edu/nutritionsource/healthy-eating-plate/
https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/324093#what-is-a-balanced-diet
https://kidshealth.org/en/parents/allergy-intolerance.html
https://www.food.gov.uk/safety-hygiene/food-allergy-and-intolerance
Sheridan, M.J., Koeberl, M., Hedges, C.E., Biros, E., Ruethers, T., Clarke, D., Buddhadasa, S., Kamath S. & Lopata, A.L. 2020. Undeclared allergens in imported packaged food for retail in Australia. Food Additives and Contaminants Part A, 37(2):183–192.
Santos, A. 2019. Why the world is becoming more allergic to food. BBC News, 13 September 2019. (Also available at: https://www.bbc.com/news/health-46302780).
https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/food-intolerance/
https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/vegetarian-diet-plan#meal-plan
Messina, V., Melina, V., & Mangels, A. R. (2003). A new food guide for North American vegetarians. Canadian Journal of Dietetic Practice and Research, 64(2), 82-86.
Haddad, E. H., Sabaté, J., & Whitten, C. G. (1999). Vegetarian food guide pyramid: a conceptual framework. The American journal of clinical nutrition, 70(3), 615s-619s.