Module 6.2: Reading
Healthy lifestyle for a greener planet
1. DIETARY / Healthy Lifestyle
The quality and source of our food has an unmistakable impact on our green environment. The volume of food consumed by humanity, as well as the increasing number of living beings on our planet, makes choices that will rapidly become radical with devastating effects.
Not only does the management of household waste represent a real challenge, but also the destination of goods and their transportation is an integral part of these challenges. What to eat, where to buy it and how to consume it, are topics to which we will try to bring a global view, in order to, measure the extent of the ecological impact and the measures that are necessary.
Learning outcomes!
- Place of supply R Resources saving
- Balanced nutrition R Healthier & less diseases
- Local & Seasonal products R Sustainability & money saving
- Balancing Food & Climate R Non processed & No food additives
- Bio Products R No drugs & no chemicals
- Learn by doing R Green habits & reflexes
Link to case studies & resources
Media Means | Resource/ Owner | Reference | Designation | LINK
|
Website
| Fourtec | Case studies | Int. food transportation | |
website | World Health Organization | Fact sheets | Healthy Diet | |
YouTube
| FIBL | Video | Organic Agricuture | |
YouTube | PhycoTerra
| Video | Soil health & Quality | |
YouTube | Fuseschool | Video | Organic farming | |
YouTube | Fuseschool | Video |
| |
YouTube | Fuseschool | Video | BIO Diversity |
2. DIETARY / Healthy Lifestyle
The quality and source of our food has an unmistakable impact on our green environment. The volume of food consumed by humanity, as well as the increasing number of living beings on our planet, makes choices that will rapidly become radical with devastating effects.
Not only does the management of household waste represent a real challenge, but also the destination of goods and their transportation is an integral part of these challenges. What to eat, where to buy it and how to consume it, are topics to which we will try to bring a global view, in order to, measure the extent of the ecological impact and the measures that are necessary.
Learning outcomes!
- Place of supply R Resources saving
- Balanced nutrition R Healthier & less diseases
- Local & Seasonal products R Sustainability & money saving
- Balancing Food & Climate R Non processed & No food additives
- Bio Products R No drugs & no chemicals
- Learn by doing R Green habits & reflexes
2.1 PLACE OF SUPPLY / Healthy Lifestyle

Often food comes from far away countries implying an important energy consumption due to a long transport by air, sea, rail & road, as well as, a consequent energy consumption for the conservation during transport.
This represents a significant energy and environmental cost, a cost that is passed on to the consumer's wallet, as well as a significant quality loss, not to mention the ecological impact.
Good to know,
3. DIETARY / Healthy Lifestyle
The quality and source of our food has an unmistakable impact on our green environment. The volume of food consumed by humanity, as well as the increasing number of living beings on our planet, makes choices that will rapidly become radical with devastating effects.
Not only does the management of household waste represent a real challenge, but also the destination of goods and their transportation is an integral part of these challenges. What to eat, where to buy it and how to consume it, are topics to which we will try to bring a global view, in order to, measure the extent of the ecological impact and the measures that are necessary.
Learning outcomes!
- Place of supply = Resources saving
- Balanced nutrition = Healthier & less diseases
- Local & Seasonal products = Sustainability & money saving
- Balancing Food & Climate = Non processed & No food additives
- Bio Products = No drugs & no chemicals
- Learn by doing = Green habits & reflexes
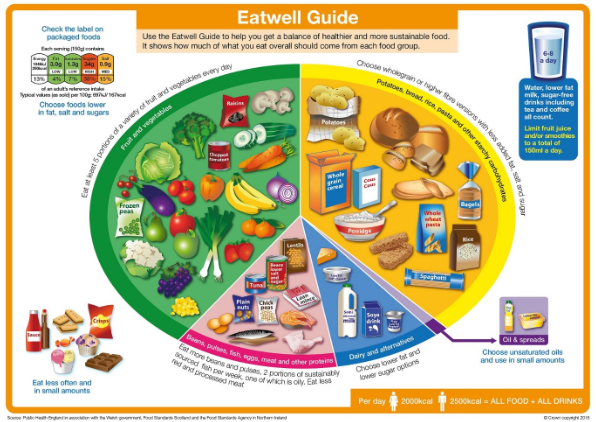
Luxembourg is very aware of the challenges of child nutrition and a rule applied throughout Luxembourg and especially in homes and school canteens is to offer free fruit to pupils at various times of the day and to encourage them to consume health food.
Since this year, the primary school benefit from free meals for all children attending school and soon this will be applied to upper schools.
This shows the importance given and very rightly to a good and balanced nutrition of children.
Good nutrition is an instinctive matter when it comes to the balance and development of children. Therefore, our project Greener Green through the programme assessment tool will ensure that this green rule would be included in the green criteria for schools.
Good to know
4. DIETARY / Healthy Lifestyle
The quality and source of our food has an unmistakable impact on our green environment. The volume of food consumed by humanity, as well as the increasing number of living beings on our planet, makes choices that will rapidly become radical with devastating effects.
Not only does the management of household waste represent a real challenge, but also the destination of goods and their transportation is an integral part of these challenges. What to eat, where to buy it and how to consume it, are topics to which we will try to bring a global view, in order to, measure the extent of the ecological impact and the measures that are necessary.
Learning outcomes!
- Place of supply R Resources saving
- Balanced nutrition R Healthier & less diseases
- Local & Seasonal products R Sustainability & money saving
- Balancing Food & Climate R Non processed & No food additives
- Bio Products R No drugs & no chemicals
- Learn by doing R Green habits & reflexes
2.3 LOCAL & SEASONNAL PRODUCTS / Healthy Lifestyle
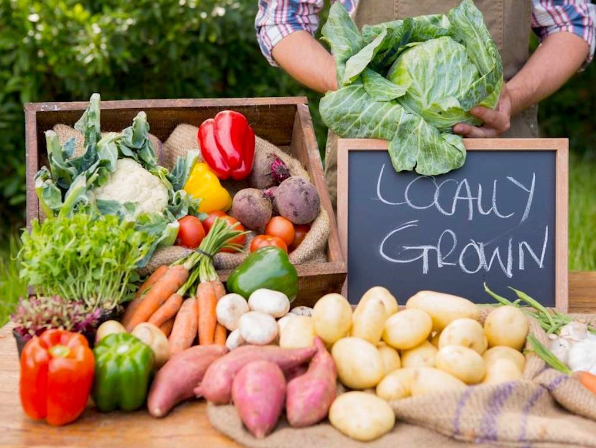

what does it mean to consume local?
As explained above, the transportation of food causes a lot of pollution as these consumable goods are transported by air, sea, rail and road.
Often the goods we consume come from far countries, traveling a long way before reaching national and regional retailers!
Beside the fact that, growing fruits and vegetables, outside of their natural season, results in significant energy overconsumption.
e.g. A summer fruit grown in winter requires heating systems that consume an unreasonable amount of energy, in order to, mimic the fruit natural growing environment.
In addition, these long transports require cooled containers during the trip to maintain freshness or simply to stop ripening, not to mention the loss of some of the food's specific nutritional characteristics.
Finally, All these interventions end up being reflected in the consumer price & on earth energetical resources.
Good to know
5. DIETARY / Healthy Lifestyle
The quality and source of our food has an unmistakable impact on our green environment. The volume of food consumed by humanity, as well as the increasing number of living beings on our planet, makes choices that will rapidly become radical with devastating effects.
Not only does the management of household waste represent a real challenge, but also the destination of goods and their transportation is an integral part of these challenges. What to eat, where to buy it and how to consume it, are topics to which we will try to bring a global view, in order to, measure the extent of the ecological impact and the measures that are necessary.
Learning outcomes!
- Place of supply R Resources saving
- Balanced nutrition R Healthier & less diseases
- Local & Seasonal products R Sustainability & money saving
- Balancing Food & Climate R Non processed & No food additives
- Bio Products R No drugs & no chemicals
- Learn by doing R Green habits & reflexes
2.4 BALANCING CLIMATE & FOOD / Healthy Lifestyle

Studies show that a diet with less meat and more vegetables would promote a green environment.
A culture of grains and vegetables would pollute and emit less carbon dioxide. In addition, the farming of grain and vegetables would provide sufficient local fodder for the animals, which would ensure a green cycle of land use, resulting in money saving & less carbon emissions and less pollution.
Good to know.
6. DIETARY / Healthy Lifestyle
The quality and source of our food has an unmistakable impact on our green environment. The volume of food consumed by humanity, as well as the increasing number of living beings on our planet, makes choices that will rapidly become radical with devastating effects.
Not only does the management of household waste represent a real challenge, but also the destination of goods and their transportation is an integral part of these challenges. What to eat, where to buy it and how to consume it, are topics to which we will try to bring a global view, in order to, measure the extent of the ecological impact and the measures that are necessary.
Learning outcomes!
- Place of supply = Resources saving
- Balanced nutrition = Healthier & less diseases
- Local & Seasonal products = Sustainability & money saving
- Balancing Food & Climate = Non processed & No food additives
- Bio Products = No drugs & no chemicals
- Learn by doing = Green habits & reflexes
2.5 BIO PRODUCTS / Healthy Lifestyle

Organic Agriculture!
When we consume BIO we undertake a gesture of vital importance for nature because we respect the natural cycle of life of the earth.
The BIO culture allows the food a freedom of forms that the chain consumption has abolished by imposing selection criteria of form, color, ...
Those Criteria that cause an impressive loss of products because products do not correspond to the label of so-called quality required for such brand or such label.
This waste of products that are fit for consumption but rejected because of secondary criteria impacts the environment, because we try to avoid overconsumption and exploit resources in all their forms according to the needs of humanity while ensuring to install a sustainable and responsible life cycle.
Good to know
7. DIETARY / Healthy Lifestyle
The quality and source of our food has an unmistakable impact on our green environment. The volume of food consumed by humanity, as well as the increasing number of living beings on our planet, makes choices that will rapidly become radical with devastating effects.
Not only does the management of household waste represent a real challenge, but also the destination of goods and their transportation is an integral part of these challenges. What to eat, where to buy it and how to consume it, are topics to which we will try to bring a global view, in order to, measure the extent of the ecological impact and the measures that are necessary.
Learning outcomes!
- Place of supply = Resources saving
- Balanced nutrition = Healthier & less diseases
- Local & Seasonal products = Sustainability & money saving
- Balancing Food & Climate = Non processed & No food additives
- Bio Products = No drugs & no chemicals
- Learn by doing = Green habits & reflexes
LEARN BY DOING / Healthy Lifestyle

Sustainable agriculture! Why is it so important to entrust a small plot of land to the little students and let them experience the contact with the earth!
It is vital to produce in a responsible and sustainable way by avoiding chemicals and GMOs, because the latter allow a thorough exploitation of the land that goes beyond its potential leading to the latter. This implies an impoverishment of the quality of the soil.
A responsible and sustainable culture, is a guarantee of environmental richness because this mode of culture leaves room for a plant and animal diversity.
We emphasize the importance of a coexistence of plants and animals, without which the land becomes arid. The animal world has a crucial activity for the aeration and the richness of the soil, as well as, the elimination of the organic waste.
Without it, the soil becomes dry, plants and trees would disappear, and the absence of trees and plants implies an absence of roots, roots that maintain the soil, without which, the soil becomes slippery and the cultivable soil is washed away, giving way to drought and desolation.
Now you know why it is so important to educate children in the small school garden.
Good to know:
Good to know: