Unit 4 - Food preparation (e-book)
4.2. Classifications and levels of standardization texture modified food
Modification of food texture and liquid thickness, without compromising the nutrient supply to ensure good health, is essential in the treatment of dysphagia.
The International Dysphagia Diet Standardization Initiative (IDDSI) Framework
The IDDSI framework consists of a continuum of 8 levels (0 - 7), where drinks are measured from Levels 0 – 4, while foods are measured from Levels 3 – 7. The IDDSI Framework provides a common terminology to describe food textures and drink thickness.
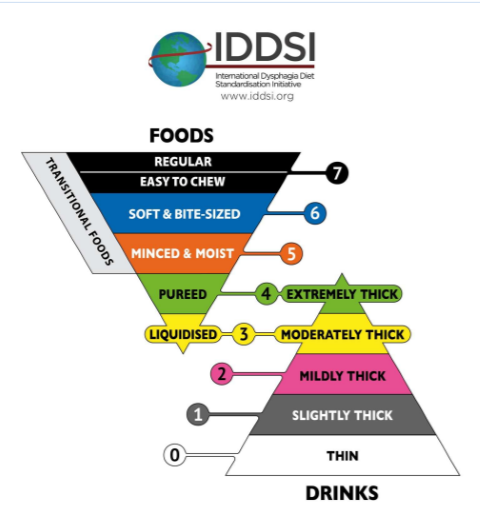
Figure 4. IDDSI classification of Foods and Drinks in 8 levels (https://iddsi.org/framework/)
Level 0: Thin
-
Flows like water
Level 1: Slightly Thick
-
Thicker than water
-
Requires a little more effort to drink than thin liquids
Level 2: Mildly Thick
-
Flows off a spoon
Level 3: Liquidiz ed/ Moderately Thick
-
Cannot be piped
-
Cannot be eaten with a fork because it drips slowly
Level 4: Pureed/ Extremely Thick
-
Cannot be drunk from a cup because it does not flow easily
-
Does not require chewing
-
Falls off spoon in a single spoonful
Level 5: Minced and Moist
-
Can be eaten with a fork or spoon
-
Can be scooped and shaped
-
Adult, equal to or less than 4mm width and no longer than 15mm in length

Go video: IDDSI Food Level Testing (Level 5 Minced and Moist)
(Source: Dorset HealthCare University NHS Foundation Trust, 2020)
Level 6: Soft and Bite-Sized
-
Can be eaten with a fork, spoon or chopsticks
-
Can be mashed/broken down with pressure from fork, spoon or chopsticks
-
Paediatric, 8mm pieces (no larger than)
-
Adults, 15 mm = 1.5 cm pieces (no larger than)

Go
video: IDDSI Food Level Testing (Level 6 Soft and Bite-sized)
(Source: Dorset HealthCare University NHS Foundation Trust, 2020)
Level 7: Easy to chew or Regular : Normal

Go
video: IDDSI Food Level Testing (Level 7 Easy to Chew)
(Source: Dorset HealthCare University NHS Foundation Trust, 2020)